What is BaaS(Blockchain As A Service) ?
Blockchain-as-a-Service represents public blockchain services that can be integrated into traditional IT architectures or Internet architectures by providing multiple ways of querying, transaction broadcasting, and transaction verification. These services were previously fragmented, including tokenization, Avatar services, and Oracle services. Now BaaS gives these services standards and specifications.
Currently, most block explorers and cryptocurrency trading platforms are built on public cloud services. Then, these platforms must build their own digital asset management and verification services in the cloud. Cloud service vendors can provide a common basic framework, just like Amazon Translate services. We can provide a derivative version of PaaS based on blockchain technology: BaaS.
Next we consider Software as a Service (SaaS). The best example of SaaS is Google Docs. Service fees for using vendor’s applications are charged based on length of use and users’ actual needs. This is the distinguishing feature of SaaS. Bitcoin is also a kind of SaaS, but Bitcoin does not have a specific cloud service provider. If we regard the Bitcoin network as an open cloud that can provide notary announcement services and transaction fees charged by block size, then we could say Bitcoin is SaaS, like the example of blockchain.info.
The diagram below can explain these concepts:
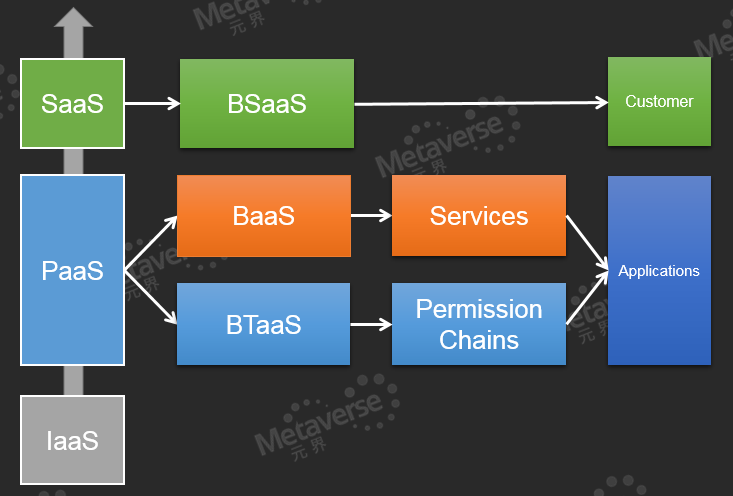
• BaaS (Blockchain As A Service) – the variant of PaaS
• BTaaS(Blockchain Technology As A Service) – the variant of PaaS
• BSaaS(Blockchain Software As A Service) – the variant of SaaS
BSaaS allows users to quickly build services directly with blockchain technology and to visualize the construction process. At present, BSaaS is not mature. There are no mature applications available currently. CryptoKitties, however, provides one example of BSaaS.
The difference here is whether to use the blockchain technology framework to build its own permissioned chain or to use the services on the public blockchain. IBM and Microsoft have proposed the former concept of BaaS. Here we change this concept into BTaaS, which can be solved through traditional IT solutions, such as using service-oriented architecture (SOA) based software to replace blockchains to build complex in-house enterprise applications.
The permissioned chain represents the activity between a few nodes and often degenerates into a game of microeconomics. Therefore, using a permissioned chain to build a collaborative system between a small number of nodes does not pose a technical challenge and evolves into how to construct a stable microeconomic model that enables collaborators to achieve Pareto improvement. In this case, the technology is secondary.
The services provided by the public blockchain are often richer than the services provided by the permissioned blockchain. If the public chain has anonymity and rights management mechanisms, the public chain can completely replace the permissioned chain.
BaaS, not BSaaS and BTaaS, concerns Metaverse the most.
BaaS means that the service provided by public blockchains will be conveniently integrated into existing internet applications and services, such as the payment function provided by Bitcoin. Metaverse will provide Avatar and MST services. For example, e-commerce providers can provide MST registration services for stores. Then the stores can issue their own bonus-point system based on the Metaverse blockchain. These bonus points share the advantages of blockchain that enable immutable P2P transactions to circulate freely on the chain.
Aggregation for Metaverse BaaS
To be wrriten…
Digital Asset Management
To be wrriten…
Aggregation with Docker
To be wrriten…
SDK supports
To be wrriten…